Development & Investment Decision Making Strategies on Private Property I
Keywords and topic
Risk Type Decision/decision making under risk, Business strategies on real estate, Real estate investment evaluation system, Mathematics analysis, Data collection, Operation research, Real estate appraising, Real estate transaction, financing, tax, and development strategies, Marketing analysis, Site, and condition analysis and simulation, Reverse engineering, Data and analysis for marketing decisions, Building design strategies, Building climate control, Life-cycle cost analysis, Construction cost estimate, Financial analysis on investment, Operation and return System Engineering, Architectural programming
Introduction: A full picture of a small size private residential property’s life cycle
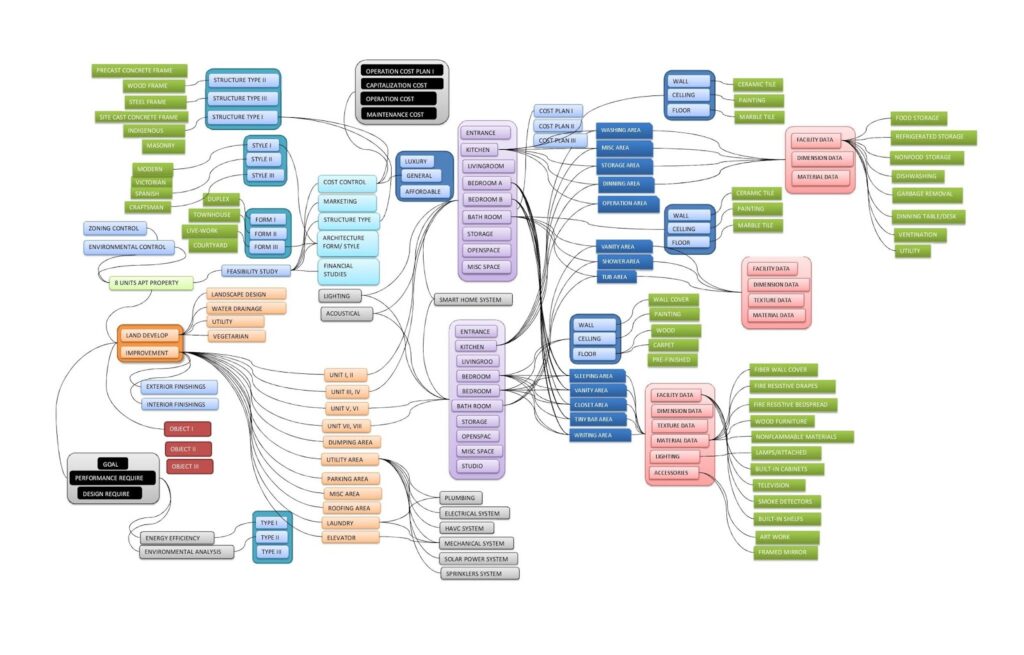
Normally, for real estate developers, there are six core stages of developing a real estate project: feasibility and acquisition, design, financing, construction, marketing and leasing, and finally is operation and management. While if zone out to a larger picture and time range, a developer occupies at the very beginning of the time period, usually around two to three years for a small to a mid-size project. considering a relatively long time for a property’s life, the majority of its life is occupied by the occupancy and tenants. As an example, once a customed built single-family house is sold out, the owners will modify it several couples of years and may sell it after a certain time. A marketing and new management process will occur, either by the seller or the listing agent. And again, it transformed to the new landlord, with different family sizes or plans for the property, for instance, transform it into a vocation or rent a property. During the transformation, the landlord may take time and budget to restore some facilities and fixtures, even the interior arrangement. This cycle will take quite a long time until some legal policy has changed on the zone for the lot, or the new investor purchase the land with the property, demolish the improvement and rebuild the entire real estate property. As a consequence, until this point, the improvement finally finishes its entire life cycle.
Here is a simplified rental property lifecycle table,
Stage I, an investor purchase the property, if a land, go to III
Stage II. demolish the improvement, or go to Stage VI
Stage III, the investor develops the land under the development principles
Stage IV, marketing for sale or leasing
Stage V, property sold, or rent out
Stage VI, if rent out, investor or third party manage the property
Stage VII, restore the property in a couple of years
Stage VIII, repeat IV to VII; if the improvement is demolished then go to Stage II
The entire process of the properties speculation for the property investors is highly complicated, that’s because not only the whole transaction workflow is full of mixture types of strategies, such as the strategies on the location selection, housing condition inspection, and mortgage brokers’ choices, evaluation on architects and engineers, but also there are branches of essential paper works, agreements, and other legal documents need to be examined very carefully within the entire or partial process of real estate activities. The entire investment action drives multiple professions and fields sufficiently interaction and deep collaboration. Besides the services assisted by third parties such as the transaction brokers, what could the real estate investors take advantage of some architectural and real estate development tools to test and get to the deep water? Take an example, could a property buyer compare the two single-family house alternatives by evaluating their basic energy consumption facts roughly at the early stage without any third parties participating? Is it possible for the buyers to have a full picture of the alternatives’ site and architectural condition in a very short time before the field trip? How and how far could big data assist those participating in the property transaction process with natural and artificial influences and facts relative to the alternatives? Is there a real-time calculation platform that easily shows the relationship between investment and profit which integrates comprehensive data from life long-term energy consumption, miscellanies expense, tax, and land price rate? Is there an easy platform to present out the Life-cycle cost analysis (LCCA) for a single-family property based on collected information and documents? The article will examine carefully on some evaluation strategies of the risk and decision-making for small and medium residence investment at architectural and development professionals’ points, which include but not limited to AHP analysis tools—a mathematical analysis tool widely used in the business and commerce field, Site Analysis Strategies—a widely applied fundamental site conditional evaluation strategy in R.E. professionals, Architectural Energy Simulation—the environmental analysis tool widely used in the architectural design process, Architectural Environmental Design Simulation—the core workflow on architectural design process which helps investors see and feel the proposal or existing property’s interior and exterior environment in three-dimensional visualization platform.
For the developers, the typical development process for the residential type of properties begins with project feasibility and acquisition, followed by design, financing, construction, marketing, and leasing. Project feasibility contains four main activities: market analysis, site selection, engineering feasibility, regulatory approvals, and financial feasibility. Usually, a third-party firm will take responsibility for the market analysis stages, which are the most essential and core part of the pre-development process. The market analysis concentrates on the problems with programming and market trends; for instance, the market analysts need to draft out what types of products are most attractive and the reasons, what is the target market, what are (potential) competitors in the market, and the facts for market demands and demographics. In the design process, architects work on the pre-design, schematic design, facility design, and working drawing process. The design principle is evidenced-based and in the meanwhile, based entirely on the market analysis in the project feasibility stage.
The ultimate objective of decision-making strategies on the properties purchased and investment process is not only to get the ideal choices but also to sharpen critical methods systematically-to be able to analyze the facts and explore potential and hidden valuable information. Relative concepts, trends, and ideas are significant to the understanding of facts. For instance, what is the real market value for the alternative which is in the buyer’s wish list? What are the historical records of the property’s real estate tax, maintenance, and utility fee? It is critical to figure out the building enclosure energy efficiency performance facts, which may have accumulated enormous utility balance. After a broader understanding, it is not hard to get close to the origin and determine factors and characteristic limitations, which will speed up the decision-making process comprehensively and systematically. For the developers and speculators, the systematically, scientifically, and logically decision techniques for investment on the existing or potential properties are only a few sequences of the life long-term investment cycle, which play such an essential part and embody the value on the entire life term investment cycle.
Mathematics Analysis Strategies (Operational research)
Operations research is often used to solve complicated tasks in real estate activities, especially to improve or optimize the efficiency of existing systems. As a branch of modern applied mathematics, Operational research focuses on the operational problems that arise in production, development, management, sale, and other activities that are solved by mathematical methods and formal science. Operational research employs a variety of approaches such as statistics, mathematical models, and algorithms to achieve the best or near-optimal solution to complex problems. Mathematical planning(Linear/nonlinear ), risk decision modelings such as the Analytic hierarchy process, Markov chain, Decision Tree, and Loss Matrix are some of the most typical operation research strategies or tools in property investment activities.
Example. Analytic hierarchy process(AHP)
Individual buyers must organize their own information collected by various means to get ready for the AHP solution. AHP is a structured technique for organizing and analyzing complex decisions, based on mathematics and psychology. It is not about finding a correct answer, instead, it helps buyers find “one that best suits their goal and their understanding of the problems.” It provides a comprehensive and rational framework for structuring a decision problem, representing and quantifying its elements, relating those elements to overall goals, and evaluating alternative solutions. “(1) Users of the AHP just decompose their decision problem into a hierarchy of more easily comprehend sub-problems, each of which can be analyzed independently. The elements of the decision problem are tangible or intangible……Once the hierarchy is built, the decision-makers systematically evaluate its various elements by comparing them to each other two at a time, with respect to their impact on an element above them in the hierarchy.”(2)
Usually, the major purposes of the buyers purchasing the properties are relocation, exchanging old houses, or property speculating. No matter how they get the final point, it is obvious that integrating the data and information they have is an ideal method for the transaction. In an AHP hierarchy for a buyer buying a property, the goal might be to choose the best property among the number of alternatives. Here are some considerations that need to be taken prior to the transaction beginning, initial cost and supplementary cost, neighborhood, local services, traffic, and occupancy as the criteria for making the decision. They might subdivide the cost criterion into the purchase price, energy costs, maintenance costs, property tax, insurance, and resale value.
In short, the process path map for AHP strategy might look like this:
Step one, first hand and second-hand information collection, the information could be the internet real estate research, local legal information, services points, market price rate, tax facts, local neighborhood, and demography information. There are some common aspects comparison lists that could be found online and in books, such as the list of architecture features conditions and local environments.
Step two, figure out criteria, this is the logical step that needs to be carefully treated.
Step three, build the hierarchy
Step four, operate the AHP program, analyze and evaluate
Step five, summary and make the conclusion, or if necessary, repeat steps two to step four
Here is one of the tremendous examples applied to the evaluation and analyzing strategies relative to real estate investment, for instance, a couple with their children are looking for a totally new property to settle in. Finding a property when the buyers are new to an area, means they are at a disadvantage since they don’t have enough valuable information to help them locate an ideal house, in a congenial location at a fair price. Conventionally, there are many aspects and features of the speculating actions that need to be examined hierarchy and logically. In real estate development and architectural design professions points, the aspect of location is at a quite unique position in their practice. As a programming strategy of development and design practice, the concept of location embodies a series of meaningful and valuable data of the market, evidence of the neighborhood’s existing condition, infrastructure, and facts of legal, historical, political, and natural features. If the buyer narrows down the aspects of decision-making criteria into a single aspect just as location, it may look like this diagram as shown the following figures.
Fig. A typical example of AHP hierarchy on location and property decision-making for three properties, modeled by the author
Fig. An example of the AHP hierarchy matrix platform, analyzed by author, system supported by http://bpmsg.com/ , K. D. Goepel